algorithm 文档
- 简历: 我精通红黑树,图结构😥😥😥【真的精通吗???🤔🤔🤔】
- 头发掉光光,呜呜呜
algorithm 数据结构是什么呐??🤔🤔
- 实际上现在的开发中基本上都是进行的是对我们的数据的增删改查吧,任何的数据都是通过我们的数据结构进行统一管理起来的呐
- 常见的数据结构含有
- 数组 -
Array - 栈 -
Stack - 链表 -
LinkedList - 图 -
Graph - 散列表 -
HashTable - 队列 -
Queue - 树 -
Tree - 堆 -
Heap
- 数组 -
algorithm 栈结构
- 栈是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的一端进行插入和删除操作,我们常说的栈就是这种数据结构,先进后出的特性吧
- 栈结构的话是可以通过我们的数组或者链表来实现的呐
last in first out
程序是如何进行执行的呐???
- 我们的程序的执行的话就涉及到了我们的栈结构的,其常用的称呼就是
函数调用栈吧 - 来个具体的例子吧
- A函数 中调用了 B函数, B函数中调用了 C函数, C函数中调用了 D函数, 那么这个函数调用栈就是 A -> B -> C -> D
- 然后结合我们的栈结构的特性,那么就是先入栈,后出栈,A 就处于栈底, D 就处于栈顶
- 那么当执行到 D 函数的时候, D 函数执行完毕之后,就会从栈顶出栈,然后执行 C 函数,
- C 函数执行完毕之后,就会从栈顶出栈, 然后执行 B 函数
- B 函数执行完毕之后,就会从栈顶出栈,然后执行 A 函数
- A 函数执行完毕之后,就会从栈顶出栈,那么整个函数调用栈就执行完毕了
栈的实现
- 实现思路
- 首先我们的栈的话是可以基于数组或者链表实现的呐
javascript
function MyStack() {
this.items = []
// 压入栈方法
MyStack.prototype.push = function(ele) {
this.items.push(ele)
}
// 弹出栈方法
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
return this.items.pop()
}
// 查看栈顶元素
MyStack.prototype.peek = function() {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1]
}
// 判断栈是否为空
MyStack.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.items.length === 0
}
// 获取栈中元素个数
MyStack.prototype.size = function() {
return this.items.length
}
// toString 方法
MyStack.prototype.toString = function() {
let resultString = ""
for(const i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
resultString += this.items[i] + " "
}
return resultString
}
}栈实现十进制转二进制
- 我们来举个例子吧,我们想把十进制的 10 转换成二进制的 1010
- 对于我们来说的话十进制转为二进制就是通过将一个数字进行不断的除以 2 来实现转换的呐
javascript
function decimalToBinary(decNumber) {
const remStack = new MyStack(); // get our stack instance
while(decNumber > 0) {
// get the remainder and save it into our stack
remStack.push(decNumber % 2);
// update the decNumber
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / 2);
}
// get our result, by popping the stack to get the remainders
let binaryString = "";
while(!remStack.isEmpty()) {
binaryString += remStack.pop().toString();
}
return binaryString;
}algorithm 队列结构
- 队列是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的一端进行插入操作,另一端进行删除操作,我们常说的队列就是这种数据结构,先进先出的特性吧
- 实际的场景的话就含有我们的:
打印队列和线程队列吧- 线程队列的话实现的思路就是我们的: 一般一个程序的话为了考虑性能的原因,
- 这个时候就需要进行的是我们的设置进程中的线程可以运行数的限制吧
- 这个时候为了让线程进行排队,这个时候就可以使用我们的队列数据结构的吧
- 先进先出的特性,但是使用队列的时候
一定要决定好我们的那一端是前端,那一端是后端,然后再进行我们的算法实现吧
- 队列的实现的话还是可以通过我们的数组和链表实现的呐
简单实现
javascript
function MyQueeu() {
// properties
this.items = []
// methods
// ele enter queue
MyQueeu.prototype.enQueue = function(ele) {
this.items.push(ele)
}
// delete queue ele
MyQueeu.prototype.deQueue = function() {
return this.items.shift()
}
// get front ele
MyQueeu.prototype.front = function() {
return this.items[0]
}
// queue isEmpty
MyQueeu.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.items.length === 0
}
// queue size
MyQueeu.prototype.size = function() {
return this.items.length
}
// queue toString
MyQueeu.prototype.toString = function() {
let resultString = ""
for(let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
resultString += this.items[i] + " "
}
return resultString
}
}使用场景 -- 击鼓传花
javascript
function passGame(nameList, num) {
const que = new MyQueeu() // get our queue instance
for(const name of nameList) {
que.enQueue(name) // add name into our queue
}
while(que.size() > 1) {
for(let i = 0; i < num - 1; i++) {
// let this delete ele reinto our queue
que.enQueue(que.deQueue())
}
// delete the ele that equal with num
que.deQueue()
}
// get winner
const winner = que.deQueue()
// return winner and its index
return [winner, nameList.indexOf(winner) + 1]
}
console.log(passGame([11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77], 3)) // [44, 4]algorithm 优先级队列
- 我们的普通的队列的话,实现添加元素的时候,是直接添加到的我们的队列的后端,但是优先级队列的话是需要考虑优先级之后再进行加入元素的呐
- 即是说我们的元素进行添加的时候,首先先进行判断优先级,然后根据优先级比较之后进行将元素添加到对应的正确位置吧
- 实际场景
- 登机顺序,急诊科排号等等都是使用我们的优先级队列来实现的呐
简单实现
- 实现的简单原理
- 需要将我们的元素和其对应的优先级组合在一起
- 添加元素的时候,将每个元素对应的优先级进行比较后,获取得到对应的正确位置后进行存放
javascript
function PriorityQueue() {
// create our priorityQueue ele class
function QueueElement(ele, priority) {
this.ele = ele
this.priority = priority
}
// properties
this.items = []
// methods
// ele into PriorityQueue method
PriorityQueue.prototype.enQueue = function(element, priority) {
const queueElement = new QueueElement(element, priority) // create queueElment
// is this priorityQueue isEmpty, save ele into our priorityQueue
if(this.items.length === 0) {
this.items.push(queueElement)
} else {
let added = false // create our flag to check our queueElement is added or not
for(let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
if(queueElement.priority < this.items[i].priority) {
this.items.splice(i, 0, queueElement) // insert ele into our priorityQueue
added = true
break
}
}
// if this queueElement is not added, save it into our priorityQueue where the end
if(!added) {
this.items.push(queueElement)
}
}
}
// delete PriorityQueue ele
PriorityQueue.prototype.deQueue = function() {
return this.items.shift()
}
// get front ele
PriorityQueue.prototype.front = function() {
return this.items[0]
}
// PriorityQueue isEmpty
PriorityQueue.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.items.length === 0
}
// PriorityQueue size
PriorityQueue.prototype.size = function() {
return this.items.length
}
// PriorityQueue toString
PriorityQueue.prototype.toString = function() {
let resultString = ""
for(let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
resultString += this.items[i].element + " " + this.items[i].priority + " "
}
return resultString
}
}algorithm 链表结构
- 链表和数组是一样的,都是一个线性的数据结构
- 但是呐,数组的内存空间的话是连续的,链表的话就不是连续的存储空间,而是一个断断续续的存储空间吧
- 链表的中的数据的话是通过我们的
指针域和数据域组合而成的吧,通过指针域实现的将每个元素实现联系起来的呐,从而达到我们线性表结构- 数组:
数组的访问元素和修改元素的性能是十分高的,但是插入和删除元素的性能十分低 - 链表:
链表的访问元素和修改元素的性能十分的低,但是插入和删除元素的性能十分的高
- 数组:
algorithm 单向链表结构
单向链表结构的实现
- 实现我们的链表结构的话,我们需要知道的就是数据结构样式,数据结构的话就是我们的
数据域 + 指针域 - 核心就是堆基本数据单元的组装吧,然后后续通过方法将我们的数据单元进行连接起来即可
javascript
function SingleLinkedList() {
// data ele
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null
}
// head ptr
this.head = null
// linkedList length
this.length = 0
// methods
// append method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.append = function(ele) {
let new_node = new Node(ele)
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = new_node
} else {
let current_node = this.head
// move to last node
while(current_node.next) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
current_node.next = new_node
}
this.length += 1
}
// insert method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.insert = function(pos, ele) {
// pos vadicate
if (pos < 0 || pos > this.length)
throw new Error("pos lastofindex....");
const new_node = new Node(ele)
if (pos === 0) {
new_node.next = this.head
this.head = new_node
} else {
let index = 1
let current_node = this.head
while (index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
new_node.next = current_node.next
current_node.next = new_node
}
this.length += 1
}
// get method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.get = function(pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.length)
throw new Error("pos lastofindex....");
let current_node = this.head
let index = 0
while(index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
return current_node
}
// indexOf method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function(data) {
let current_node = this.head
let index = 0
while(current_node) {
if(current_node.data === data) {
return index
}
current_node = current_node.next
index += 1
}
return -1
}
// update method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.update = function(pos, ele) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.length)
throw new Error("pos lastofindex....");
let current_node = this.head
let index = 0
while(index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
current_node.data = ele
}
// removeAt method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.length)
throw new Error("pos lastofindex....");
let pre_node = this.head
if(pos === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next
return
}
let index = 1
while(index++ < pos) {
pre_node = pre_node.next
}
let del_node = pre_node.next
pre_node = pre_node.next.next
del_node = null
this.length -= 1
}
// remove method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.remove = function(ele) {
this.removeAt(this.indexOf(ele))
}
// isEmpty method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.length === 0
}
// size method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.size = function() {
return this.length
}
// toString method
SingleLinkedList.prototype.toString = function() {
let current_node = this.head
let listString = ""
while(current_node) {
listString += current_node.data.toString() + " "
current_node = current_node.next
}
return listString
}
}algorithm 双向链表结构
- 单向链表只能从我们的头指针遍历到尾部
- 但是我们的双向链表可以实现的是我们的双向的遍历吧,双向链表的数据结构为:
pre指针 + data域 + next指针
- 对于我们的编程语言来说,实现我们的数据结构和算法的话,最主要的就是构建出我们自身所需要的结构类型吧
比如说我们的很多语言中并没有内置的数据结构,只有一个数组结构罢了,这个时候就需要使用我们的自定义数据结构来实现吧
- 双向链表的缺点
- 占用的内存空间更大以及实现难度更大
双向链表的实现
javascript
function DoubleLinkedList() {
// ele struct
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.pre = null
this.next = null
}
// pproperties
this.head = null
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
// methods
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.append = function(data) {
let new_node = new Node(data)
if(this.length === 0) {
this.head = new_node
} else {
let current_node = this.head
while(current_node.next) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
current_node.next = new_node
new_node.pre = current_node
}
this.tail = new_node
this.length += 1
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.insert = function(pos, data) {
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.length)
throw new Error("index lastofIndexRange....");
let new_node = new Node(data)
if(this.length === 0) {
this.head = new_node
this.tail = new_node
} else {
if (pos === 0) {
this.head.pre = new_node
new_node.next = this.head
this.head = new_node
} else if(pos === this.length) {
new_node.pre = this.tail
this.tail.next = new_node
this.tail = new_node
} else {
let current_node = this.head
let index = 0
while(index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
new_node.next = current_node
new_node.pre = current_node.pre
current_node.pre.next = new_node
current_node.pre = new_node
}
}
this.length += 1
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.get = function(pos) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.length)
throw new Error("index lastofIndexRange....");
let current_node = this.head
let index = 0
while(index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
return current_node.data
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function(data) {
let index = 0
let current_node = this.head
while (current_node) {
if (current_node.data === data) return index
current_node = current_node.next
index += 1
}
return -1
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.update = function(pos, new_data) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.length)
throw new Error("index lastofIndexRange....");
let index = 0
let current_node = this.head
while (index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
current_node.data = new_data
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(pos) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.length)
throw new Error("index lastofIndexRange....");
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head.pre = null
this.head.next = null
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
if (pos === 0) {
let del_node = this.head
this.head.next.pre = null
this.head = this.head.next
del_node.next = null
del_node.pre = null
} else if (pos === this.length - 1) {
this.tail.pre,next = null
this.tail = this.tail.pre
} else {
let index = 0
let current_node = this.head
while (index++ < pos) {
current_node = current_node.next
}
current_node.pre.next = current_node.next
current_node.next.pre = current_node.pre
current_node.pre = null
current_node.next = null
}
}
this.length -= 1
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.remove = function(data) {
this.removeAt(this.indexOf(data))
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.length === 0
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.size = function() {
return this.length
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.toString = function(isBack = true) {
return isBack ? this.backwardString() : this.forwardString()
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.forwardString = function() {
let current_node = this.tail
let resultString = ""
while(current_node) {
resultString += current_node.data.toString() + " "
current_node = current_node.pre
}
return resultString
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.backwardString = function() {
let current_node = this.head
let resultString = ""
while(current_node) {
resultString += current_node.data.toString() + " "
current_node = current_node.next
}
return resultString
}
}algorithm 集合结构
- 集合最常见的就是我们的哈希表吧
- 集合的特点,
内部的元素无须且不重复 - 就是一个特殊的数组吧,js 里面对应的就是我们的
Set 和 WeakSet
- 集合的特点,
集合简单实现
javascript
function MySet() {
// properties
this.items = {}
// methods
MySet.prototype.add = function(value) {
if (this.has(value)) return false
this.items[value] = value
return true
}
MySet.prototype.has = function(value) {
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(value)
}
MySet.prototype.remove = function(value) {
if (!this.has(value)) return false
delete this.items[value]
}
MySet.prototype.clear = function() {
for(let key of Object.keys(this.items)) {
delete this.items[key]
}
}
MySet.prototype.size = function() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length
}
MySet.prototype.values = function() {
return Object.keys(this.items)
}
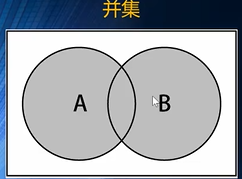
}集合的并集
- 集合并集就是返回一个包含所有集合的新的元素吧
javascript
function getUnionSet(set, newSet) {
const unionSet = new Set()
for(let value of set) {
unionSet.add(value)
}
for(let value of newSet) {
if (unionSet.has(value)) continue
else unionSet.add(value)
}
return unionSet
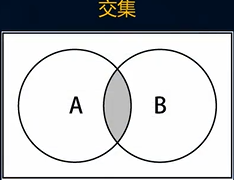
}集合的交集
- 集合的交集就是返回多个集合共同具备的元素吧
javascript
function getInterSectionSet(set, otherSet) {
const new_set = new Set()
for (const val of set) {
// core
if (otherSet.has(val))
new_set.add(val)
}
return new_set
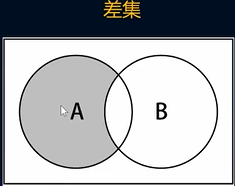
}集合的差集
- 集合的差集就是返回一个集合,该集合包含第一个集合,但是第二个集合没有的元素
javascript
function getDifferenceSet(set, otherSet) {
const new_set = new Set()
for (const val of set) {
// core
if (!otherSet.has(val))
new_set.add(val)
}
return new_set
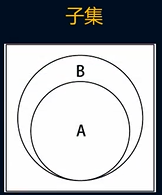
}集合的子集
- 集合的子集就是判断一个集合是否是另一个集合的子集
javascript
function isSubset(set, otherSet) {
for (const val of set) {
// core
if (!otherSet.has(val))
return false
}
return true
}algorithm 哈希表结构
- 在不同的编程语言对其的称呼有一定的不同,但是本质的话是通过键值对的形式进行存储的我们的数据单元的呐
- JS 里面我们使用
Map来实现哈希表,python 中就是dict字典,Java 中就是HashMap和TreeMap - 为什么需要了解哈希表呐??
- 哈希表本身提供了非常快的
插入-删除-查找操作 - 无论数据规模有多大,对于哈希表的
插入和删除操作的时间复杂度都是常数级的 - 哈希表的速度比树的速度还快,可以实现瞬间查找得到我们想要的元素吧
- 哈希表本身提供了非常快的
- 哈希表到底是什么呐??
- 哈希表的实现基于数组,但是在哈希表的实现过程中使用了哈希函数,通过
哈希函数实现获取得到我们的HashCode - 这个就是我们的 HashTable 的独特之处了吧,通过我们的 hashCode 实现迅速的获取得到我们需要查找的元素吧
- 哈希表的实现基于数组,但是在哈希表的实现过程中使用了哈希函数,通过
认识哈希化
- 哈希化就是实现的是我们的将大数字转化为数组范围内的一种过程
- 哈希函数: 就是实现的是将单词转化为大数字,然后实现对应的大数字哈希化的操作,这个函数就是我们的哈希函数
- 哈希表: 就是实现的我们的哈希化,然后通过哈希化的结果,实现我们的哈希表
认识哈希冲突
- 也就是在我们的哈希化的过程中可能导致的是具备我们的哈希函数得出的数字是冲突的,这个时候就需要进行对应的解决
- 解决方案就包含两种
链地址法开放寻址法
链地址法
- 也就是实现的是在我们的哈希表对应的位置上进行我们的使用链表使用我们的元素的链接起来即可吧
- 也就是说我们的哈希表中每个位置对应的是我们的一个
数组或者说是链表吧- 选择链表更加方便吧,因为我们地插入含有我们的插入
前端或者说后端吧- 对于链表删除和插入是十分方便的呐
- 对于数组的话,我们的查找元素以及更新元素是更加方便的吧
- 选择链表更加方便吧,因为我们地插入含有我们的插入
开放寻址法
- 就是实现的是我们的那里有缺的就吧元素往那个位置插入即可吧
- 在实现查找空位的时候,我们可以使用的方法为:
线性探测- 就是通过我们的步长为1,一点点的来寻找我们的空白单元的呐,查找过程中,一定遇到了空白位置直接停止查找的呐
- 删除的时候用 -1 来代替吧
二次探测再哈希法
哈希函数的指标
霍纳法则
- 实现快速的计算
- 快速的哈希函数的话主要是想解决的是我们的快速得到对应的 hashCode 即可吧
- 实现均匀的分布
- 主要是实现的是对我们的hashCode进行压缩,然后实现我们的哈希表,哈希表实现对应的均匀分布吧
实现哈希函数
- 主要是通过的是我们的字符串的 charCodeAt 来实现的呐,该方法主要是获取字符的unicode编码的呐
- 然后通过我们的 37 来做为我们的压缩哈希码的哈希函数
javascript
// 实现hash函数
// ==> hashCode ==> 压缩hashCode ==> 映射到数组范围
/**
* 实现hash函数
* @param str 需要进行哈希化的字符串
* @param max 长度
*/
function hashFunc(str, max) {
let hashCode = 0
// 霍纳算法实现计算hashCode的值
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hashCode = 37/*一定是一个质数,一般是这个数字吧*/ * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i) //或者 charCodeAt(i)的unicode编码
}
// 压缩hashCode
let index = hashCode % max
return index
}实现哈希表
- 实现的基本思路为:
- 属性的定义
this.storage是用于实现存储的数组this.count是用于实现哈希表存储的元素个数this.limit是用于实现哈希表存储的数组的长度
- 实例方法的定义
HashFunc(str, size)是用于实现哈希化的方法,内部使用霍纳法则实现吧put(key, value)该方法中具备了对应的插入和更新操作get(key)该方法中具备了对应的查找操作remove(key)该方法中具备了对应的删除操作resize(newLimit)该方法中具备了对应的哈希表扩容操作
- 属性的定义
- 一定要确保我们的数字为质数,这样我们的哈希化过程,就会更加均匀
javascript
// 实现hashtable
function HashTable() {
// define property
this.storage = [] // 存储
this.count = 0 // 长度,后面根据我们的装载因子来判断是否需要进行扩容,装载因子一般是为0.75吧
this.limit = 7 // 长度
this.loadFactor = 0.75 // 装载因子,后面根据我们的装载因子来判断是否需要进行扩容,装载因子一般是为0.75吧
// define method
/**
* 实现hashFunc函数,实现对应的生成hashCode 的值吧
* @param {string} str
* @param {number} size
* @returns {number}
*/
HashTable.prototype.HashFunc = function (str, size) {
let hashCode = 0
// 1. 霍纳法则,计算hashCode的值
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i)
}
return hashCode % size
}
/**
* 实现put方法,添加元素
* @param {string} key
* @param {string} value
*/
HashTable.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
// 基本的结构为: [[[key, value], [key, value]], [[key, value], [key, value]]]
let index = this.HashFunc(key, this.limit) // 生成对应的索引
let bucket = this.storage[index] // 取出对应的bucket
if (bucket === undefined) { // 如果bucket不存在,就创建一个bucket
bucket = []
this.storage[index] = bucket
}
// 1. 判断是新增还是修改原来的值
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i] // 取出对应的元组
if (tuple[0] === key) {
tuple[1] = value
return
}
}
// 2. 进行新增元素即可
bucket.push([key, value])
this.count += 1
// 3. 判断是否需要扩容
if (this.count > this.limit * this.loadFactor) {
this.expend() // 扩容
}
}
/**
* 实现get方法,获取元素
* @param {string} key
* @returns
*/
HashTable.prototype.get = function (key) {
let index = this.HashFunc(key, this.limit) // 获取对应的index
let bucket = this.storage[index] // 获取对应的bucket
if (bucket === undefined) return null // 如果bucket不存在,就返回null
// 1. 遍历bucket,查找是否有对应的key
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i] // 取出对应的元组
if (tuple[0] === key) {
return tuple[1]
}
}
return null // 如果没有找到,就返回null
}
/**
* 实现remove方法,删除元素
* @param {string} key
* @returns {string|null}
*/
HashTable.prototype.remove = function (key) {
let index = this.HashFunc(key, this.limit) // 获取对应的index
let bucket = this.storage[index] // 获取对应的bucket
if (bucket === undefined) return null // 如果bucket不存在,就返回null
// 1. 遍历bucket,查找是否有对应的key
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let tuple = bucket[i] // 取出对应的元组
if (tuple[0] === key) {
bucket.splice(i, 1) // 删除对应的元组
this.count -= 1 // 长度减1
// 2. 判断是否需要缩容
if (this.count < this.limit * (1 - this.loadFactor)) {
this.shrink() // 缩容
}
return `成功删除${tuple}` // 返回对应的value
}
}
return null // 如果没有找到,就返回null
}
/**
* isEmpty 判断hashTable是否为空
* @returns {boolean}
*/
HashTable.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.count === 0
}
/**
* size 获取hashTable的长度
* @returns {number}
*/
HashTable.prototype.size = function () {
return this.count
}
/**
* resize 重新调整hashTable的长度
* @param {number} newLimit
*/
HashTable.prototype.resize = function (newLimit) {
// 1. 保存旧的storage
let oldStorage = this.storage
// 2. 重置所有的属性
this.storage = []
this.count = 0
this.limit = newLimit
// 3. 遍历oldStorage中的所有bucket
for (let i = 0; i < oldStorage.length; i++) {
let bucket = oldStorage[i] // 取出对应的bucket
if (bucket === undefined) continue // 如果bucket不存在,就跳过
// 4. 遍历bucket,取出所有的元组
for (let j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) {
let tuple = bucket[j] // 取出对应的元组
this.put(tuple[0], tuple[1]) // 重新插入
}
}
}
/**
* expend 扩容
*/
HashTable.prototype.expend = function () {
// 确保是质数
let newLimit = Math.floor(this.limit * this.loadFactor + this.limit)
while (!this.isPrime(newLimit)) {
newLimit += 1 // 一直找到质数为止
}
this.resize(newLimit)
}
/**
* shrink 缩容
*/
HashTable.prototype.shrink = function () {
let newLimit = Math.floor(this.limit * this.loadFactor)
while (!this.isPrime(newLimit)) {
newLimit -= 1 // 一直找到质数为止
}
this.resize(newLimit)
}
/**
* 判断是不是质数
* @param {number} num
* @returns {boolean}
*/
HashTable.prototype.isPrime = function (num) {
let temp = parseInt(Math.sqrt(num)) // 取平方根
for (let i = 2; i <= temp; i++) { // 遍历
if (num % i === 0) { // 如果能被整除,就不是质数
return false
}
}
return true // 如果不能被整除,就是质数
}
}algorithm 树结构
- 树结构的话一般都是包含我们的根的呐
- 同时在根的基础上都是会分出一个一个的分支吧
- 类似我们的一个公司的组织架构吧,就类似于我们的一个树结构吧
树结构优点
- 树结构的话也是一个用来保存我们数据的一种可选的方式吧
- 利用树结构的话,可以实现的是: 我们可以很方便的去查找我们的数据
- 树结构的空间利用率是十分高的呐
- 同时树结构可以按照特定的排序来实现存储我们的元素吧
树结构的术语
树 tree由n>=0的节点构成的有限集合根 root是一个特殊的节点,没有父节点子树 subtree是节点的一个分支节点的度 degree是节点的子树数目叶子节点 leaf node是没有子树的节点高度 height是从根到叶子的最长路径的节点数路径 path是从根节点到叶子节点的节点序列路径长度 path length根节点到叶子节点的路径长度,边的个数,不是节点的个数满树 full tree是所有节点的度都为k的树二叉树 binary tree是由节点组成的树,其中每个节点最多有2个子节点满二叉树 full binary tree是由节点组成的树,其中每个节点最多有2个子节点,并且所有的叶子节点都在同一层父节点 parent node子节点 child node兄弟节点 sibling node节点层次 level
algorithm 二叉树
- 就是每个节点后最多只有两个子节点吧,这个就是我们的二叉树了吧
- 二叉树定义
- 二叉树可以为空,也就是没有任何的节点
- 若不为空,二叉树只能你每个子节点最多两个子节点吧
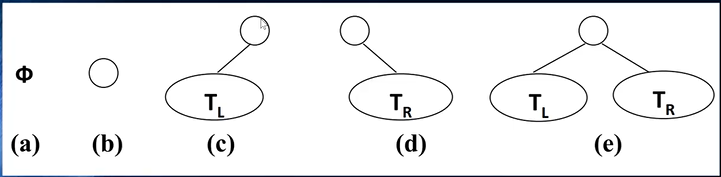
- 二叉树的五种状态:
空节点状态单节点状态只具备左子节点状态只具备右子节点状态具备左右子节点状态
二叉树特性
- 每一层的子节点个数推导
- 根节点的子节点: 第一层的子节点个数,也就是最多
2个 - 第二层的子节点个数: 第一层的子节点个数 * 2,也就是最多
4个 - 第三层的子节点个数: 第二层的子节点个数 * 2,也就是最多
8个 - ……依次类推
- 根节点的子节点: 第一层的子节点个数,也就是最多

完美二叉树 Perfect Binary Tree
- 完美二叉树就是二叉树的一种,它的特点是:
- 每一个节点的子节点都是
2个,且层之间是不缺失的
- 每一个节点的子节点都是
完全二叉树 Complete Binary Tree
- 完全二叉树就是二叉树的一种,它的特点是:
- 也就是还是保持的是二叉树的特性,但是最后一层有缺失存在吧
除了我们的叶子节点之外,其他的节点都是满的
二叉树使用方案
- 使用数组来实现
- 最终的实现方案还是通过我们的完美二叉树的补充来实现吧
- 缺失的部分进行对应补充即可,但是具备空间的浪费
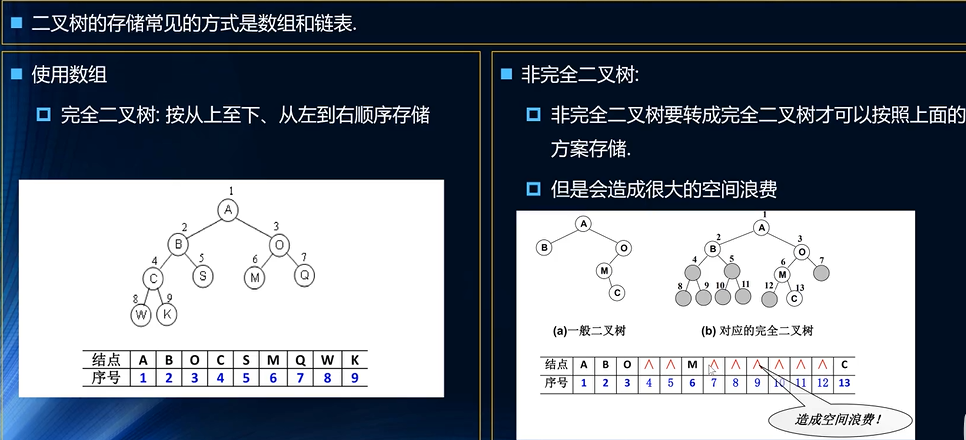
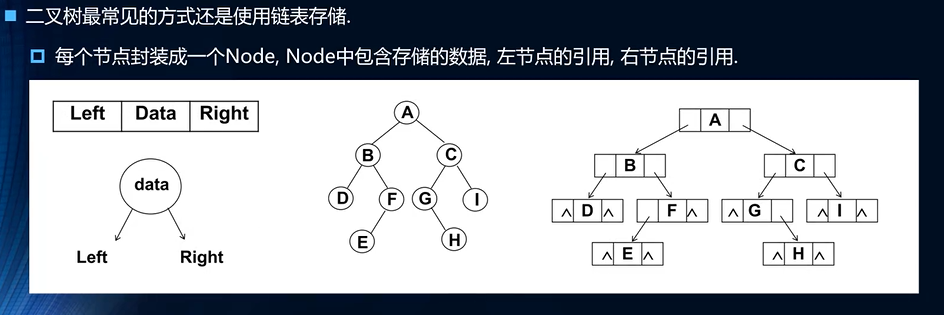
- 使用链表来实现
- 这样的方式是最常见的吧
- 同时大量的节省了我们的很多的空间占用吧
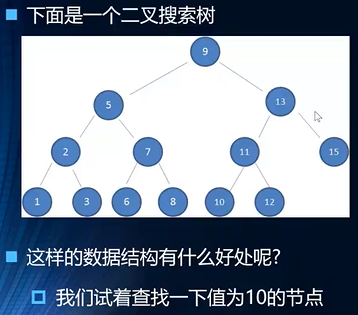
algorithm 二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树 BST
binary search tree
二叉搜索树特点
- 可以为空
- 如果不为空的话,性质为:
- 非空左子树所有键值
小于其根节点的键值 - 非空右子树所有键值
大于其根节点的键值 - 左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
- 非空左子树所有键值
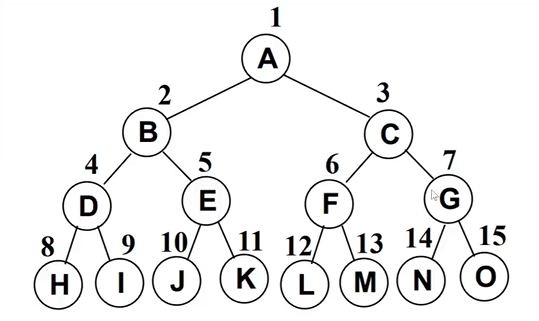
- 举个例子
- 如图所示,我们的查找过程只需要在节点之间进行比较3次即可寻找到我们的需要寻找的元素吧
- 如果说我们使用单纯链表的数据结构,那么我们查找的复杂度就变成了
O(n)
二叉搜索树实现
- insertNode 插入节点实现
- insert 插入实现
- max 获取最大值
- min 获取最小值
- search 根据key实现寻找节点
- 先序遍历
访问节点先序遍历其左子树先序遍历其右子树
- 中序遍历
中序遍历其左子树访问节点中序遍历其右子树
- 后序遍历
后续遍历其左子树后续遍历其右子树访问节点
- remove 删除节点操作
- 首先查找得到节点的位置
- 删除分为三种情况吧
查找到的都是叶子节点- 此时直接删除即可
查找到的只有一个子节点- 也是直接删除,让其父节点指向其下一个节点即可
查找到的都是有两个子节点左边找最大,右边找最小进行对应的节点替换吧
javascript
function BinarySearchTree() {
function Node(key) {
this.key = key; // 节点的键值
this.left = null; // 左子节点
this.right = null; // 右子节点
}
// define property of root node
this.root = null; // 根节点
/**
* 插入节点吧
* @param {Node} node
* @param {Node} newNode
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.insertNode = function(node, newNode) {
// use recursion to insert node,while the node is null,insert node
if (newNode.key < node.key) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
// insert method
/**
* insert node to the tree
* @param {*} key
* @param {*} value
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.insert = function(key) {
// 1. create node
let newNode = new Node(key);
// 2. insert node
// 2.1 if the tree is empty, insert node as root
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 2.2 find the position to insert node
let current = this.root;
this.insertNode(current, newNode);
}
}
/**
* minimum value in the tree
* @returns the minimum value in the tree
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.min = function() {
let current = this.root;
// if the tree is empty, return null
if (current === null) return null;
// find the leftmost node
while (current && current.left !== null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.key;
}
/**
* maximum value in the tree
* @returns the maximum value in the tree
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.max = function() {
let current = this.root;
// if the tree is empty, return null
if (current === null) return null;
// find the rightmost node
while (current && current.right!== null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.key;
}
/**
* 搜索指定的节点
* @param {*} key
* @returns {Node|null} Node or null
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.search = function(key) {
let current = this.root;
// if the tree is empty, return null
if (current === null) return null;
// find the node with the key
while (current && current.key!== key) {
if (key < current.key) {
current = current.left;
} else if (key > current.key) {
current = current.right;
} else {
return current;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 先序遍历
* 1. 访问根节点
* 2. 对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
* 3. 对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历
* @param {Node} node
* @param {Function} handler
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.preOrderTraverseNode = function(node, handler) {
if (node !== null) {
// settle the handler function
if (handler) {
// 处理每一个经过的节点
handler(node.key);
// 对左子树进行先序遍历
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, handler);
// 对右子树进行先序遍历
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, handler);
}
}
}
BinarySearchTree.prototype.preOrderTraversal = function(handler) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, handler);
}
/**
* 中序遍历
* 1. 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
* 2. 访问根节点
* 3. 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
* @param {Node} node
* @param {Node} node
* @param {Function} handler
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.middleOrderTraverseNode = function(node, handler) {
if (node!== null) {
if (handler) {
// 对左子树进行中序遍历
this.middleOrderTraverseNode(node.left, handler);
// 处理每一个经过的节点
handler(node.key);
// 对右子树进行中序遍历
this.middleOrderTraverseNode(node.right, handler);
}
}
}
BinarySearchTree.prototype.middleOrderTraversal = function(handler) {
this.middleOrderTraverseNode(this.root, handler);
}
/**
* 后序遍历
* 1. 对根节点的左子树进行后序遍历
* 2. 对根节点的右子树进行后序遍历
* 3. 访问根节点
* @param {Node} node
* @param {Function} handler
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.postOrderTraverseNode = function(node, handler) {
if (node!== null) {
if (handler) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, handler);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, handler);
handler(node.key);
}
}
}
BinarySearchTree.prototype.postOrderTraversal = function(handler) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, handler);
}
/**
* remove node from the tree
* @param key
* @return {boolean}
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.remove = function(key) {
let current = this.root;
let parent = null;
let isLeftChild = true;
// find the node with the key
// if the tree is empty, return false
while (current && current.key!== key) {
parent = current;
if (key < current.key) {
current = current.left;
isLeftChild = true;
} else if (key > current.key) {
current = current.right;
isLeftChild = false;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// remove leaf node
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
if /* 叶子节点为根节点 */ (current === this.root) {
this.root = null;
} /* 叶子节点为左节点 */ else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = null;
} /* 叶子节点为右节点 */ else {
parent.right = null;
}
}
// remove single child node
if (current.right === null) {
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.left;
}
if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = current.left;
} else {
parent.right = current.left;
}
} else if (current.left === null) {
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.right;
}
if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = current.right;
} else {
parent.right = current.right;
}
}
// remove double child node
if (current.left !== null && current.right !== null) {
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.right;
current.right.left = current.left;
}
if (isLeftChild) {
//寻找到左子树的最大节点
let maxNode = current.left;
while (maxNode.right !== null) {
maxNode = maxNode.right;
}
// 进行替换节点
parent.left = maxNode;
maxNode.right = current.right;
maxNode.left = current.left;
} else {
//寻找到右子树的最小节点
let minNode = current.right;
while (minNode.left !== null) {
minNode = minNode.left;
}
// 进行替换节点
parent.right = minNode;
minNode.left = current.left;
minNode.right = current.right;
}
}
delete current;
return true; // 删除成功
}
/**
* get height of the tree, 二叉树的效率取决于我们的树的深度
* @param node
* @return {number}
*/
BinarySearchTree.prototype.getHeight = function(node) {
if (node === null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(this.getHeight(node.left), this.getHeight(node.right)) + 1;
}
}algorithm 平衡二叉树
- 主要是为了实现我们的二叉树的数据中根节点的选取至关重要吧
- 根节点的选择,实现我们的保证树结构的平衡性的吧
AVL 树也是一个保持平衡二叉树的一种方案吧红黑树也是一个平衡二叉树的一种实现方案吧
algorithm 红黑树
认识红黑树
节点是红色或者说黑色根节点是黑色- 每个叶子节点都是
黑色的空节点 - 每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色
- 从任意节点到其叶子节点的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点
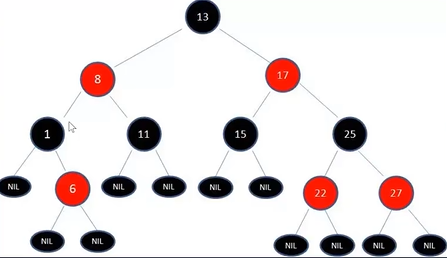
红黑树的变换
- 也就是我们的树结构中的颜色变化吧
- 红黑树的变化的话具备我们的
- 换色 --> 左旋转 --> 右旋转
左旋转就是我们的逆时针旋转吧,具备的子节点进行平移即可右旋转就是我们的顺时针旋转吧,具备的子节点进行平移即可
- 换色 --> 左旋转 --> 右旋转
- 为了符合我们的红黑树的基本规则,这个时候需要进行我们的红黑色的变换吧
- 一般的话我们的
插入的新的节点的话一般是我们的红色吧- 名称约束
- 新插入的节点称之为:
N-- New - 插入的新节点对应的父节点:
P-- Parent - 插入的新节点对应的祖父节点:
G-- GrandParent - 插入的新节点对应的叔叔节点:
U-- Uncle
- 新插入的节点称之为:
- 名称约束
- 只能说,十分的难,这里就不写代码了,草!!!
- 变化的规则一共五种,
难崩 - 背都背不住,还写代码,梦呐,呜呜呜😭😭😭
- 变化的规则一共五种,
algorithm 图结构
认识图结构
- 图结构和我们的树结构是十分相似的呐
- 主要是研究
顶点和边组成的数学理论和方法顶点代表一个一个的事物,边代表每个事物之间的关系- 人与人之间的关系网
图的相关术语
顶点:图中的一个点,可以有任意数量的顶点。相邻顶点: 与当前顶点相邻的顶点。边:顶点之间连接的线或弧,可以有任意数量的边。路径:顶点之间连接的边序列,称为路径。图:由顶点和边组成的数学对象。无向图:图中的边没有方向,即边是双向的。有向图:图中的边有方向,即边是单向的。度: 相邻顶点数量。连通图:图中的任意两个顶点之间都存在路径。连通分量:连通图的子集,其中每个子集都是连通的。无权图:图中的边没有权重。带权图:图中的边有权重。
图的表示方法
邻接矩阵的表示方法,主要是通过我们的二维数组来表示我们的图结构的呐邻接表的表示方法,主要是通过我们的链表来表示我们的图结构的呐
图的遍历算法
- 每一个顶点对应的邻接表,使用我们的映射表来进行存储吧
- 广度优先搜索
Breadth-first search (BFS)- 实现的是一直遍历到尾即可,直到没有任何的子节点的时候直接退出即可
- 深度优先搜索
Depth-first search (DFS)- 实现的是确保每个通路全部遍历完,否则就不退出,退出的标志是重新回归到我们的初始位置吧
- 进行实现我们的遍历的时候,首先需要指定初始节点吧
- 每个节点内部保存的状态设置
- 没有被访问过的状态 -- '0'
- 被访问过的状态,但是没有被探索过 -- '1'
- 被访问过的状态,并且被探索过的状态 -- '2'
javascript
function Dict() {
//todo: define property
this.data = {}; // map also can use
//todo: define methods
Dict.prototype.set = function (key, value) {
this.data[key] = value;
}
Dict.prototype.get = function (key) {
return this.data[key];
}
Dict.prototype.remove = function (key) {
delete this.data[key];
}
Dict.prototype.has = function (key) {
return this.data.hasOwnProperty(key);
}
Dict.prototype.size = function () {
return Object.keys(this.data).length;
}
Dict.prototype.clear = function () {
this.data = {};
}
Dict.prototype.keys = function () {
return Object.keys(this.data);
}
}
function Queue() {
//todo: define property
this.data = []; // 存储队列元素的数组
//todo: define methods
/**
* 入队
* @param {*} element
*/
Queue.prototype.enqueue = function (element) {
this.data.push(element); // 向数组的末尾添加元素
}
/**
* 出队
* @returns {*}
*/
Queue.prototype.dequeue = function () {
return this.data.shift(); // 从数组的开头删除元素
}
/**
* 查看队列的第一个元素
* @returns {*}
*/
Queue.prototype.front = function () {
return this.data[0]; // 返回数组的第一个元素
}
/**
* 查看队列是否为空
* @returns {boolean}
*/
Queue.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.data.length === 0; // 返回数组的长度是否为0
}
/**
* 查看队列的大小
* @returns {number}
*/
Queue.prototype.size = function () {
return this.data.length; // 返回数组的长度
}
/**
* 清空队列
*/
Queue.prototype.clear = function () {
this.data = []; // 将数组的长度设置为0
}
/**
* 打印队列
*/
Queue.prototype.toString = function () {
let str = ''; // 定义一个字符串变量,用于存储队列的元素
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) { // 遍历数组
str += this.data[i] + " "; // 将数组的元素添加到字符串中
}
return str; // 返回字符串
}
Queue.prototype.print = function () {
console.log(this.data.toString()); // 将数组转换为字符串并打印
}
}
function Graph() {
//todo: define properties
this.vertices = []; // 顶点数组
this.edges = new Dict(); // 边数组
//todo: define methods
/**
* 定义顶点
* @param {*} vectex
*/
Graph.prototype.addVartex = function (vectex) {
this.vertices.push(vectex);
this.edges.set(vectex, []); // 初始化边数组
}
/**
* 定义边
* @param {*} vectex1
* @param {*} vectex2
*/
Graph.prototype.addEage = function (vectex1, vectex2) {
this.edges.get(vectex1).push(vectex2); // 向边数组中添加边
this.edges.get(vectex2).push(vectex1); // 向边数组中添加边
}
/**
* 打印图
*/
Graph.prototype.toString = function () {
let str = '';
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices.length; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
str += this.vertices[i] + " -> " // 打印顶点
let neighbors = this.edges.get(this.vertices[i]); // 获取边数组
for (let j = 0; j < neighbors.length; j++) { // 遍历边数组
str += neighbors[j] + " "; // 打印边
}
str += "\n"; // 换行
}
return str;
}
/**
* 初始化顶点状态
* '0' 未被访问
* '1' 被访问,但是未探索
* '2' 被访问,并且被探索
*/
Graph.prototype.initState = function () {
let states = [] // 存储顶点的状态
for (let i = 0; i < this.vertices.length; i++) { // 遍历顶点数组
states[this.vertices[i]] = '0'; // 初始化顶点的状态,和顶点数组的索引对应
}
return states; // 返回顶点的状态
}
/**
* 广度优先搜索
* @param {*} initVectex
* @param {*} callback
*/
Graph.prototype.bfs = function (initVectex, callback) {
let states = this.initState(); // 初始化顶点状态
let queue = new Queue(); // 创建队列
queue.enqueue(initVectex); // 将初始顶点入队
while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // 当队列不为空时
let vectex = queue.dequeue(); // 出队
let neighbors = this.edges.get(vectex); // 获取边数组
states[vectex] = '1'; // 将顶点的状态设置为1
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) { // 遍历边数组
let n = neighbors[i]; // 获取边数组的元素
if (states[n] === '0') { // 如果顶点的状态为0
states[n] = '1'; // 将顶点的状态设置为1
queue.enqueue(n); // 将顶点入队
}
callback(vectex, n); // 调用回调函数
states[vectex] = '2'; // 将顶点的状态设置为2
}
}
}
/**
* 深度优先搜索
* @param {*} initVectex
* @param {*} callback
*/
Graph.prototype.dfs = function (initVectex, callback) {
let states = this.initState(); // 初始化顶点状态
this.dfsVisit(initVectex, states, callback); // 调用dfsVisit方法
}
/**
* 递归调用dfsVisit方法
* @param {*} vectex
* @param {*} states
* @param {*} callback
*/
Graph.prototype.dfsVisit = function (vectex, states, callback) {
states[vectex] = '1'; // 将顶点的状态设置为1
let neighbors = this.edges.get(vectex); // 获取边数组
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) { // 遍历边数组
let n = neighbors[i]; // 获取边数组的元素
if (states[n] === '0') { // 如果顶点的状态为0
this.dfsVisit(n, states, callback); // 递归调用
}
callback(vectex, n); // 调用回调函数
states[vectex] = '2'; // 将顶点的状态设置为2
}
}
}algorithm 排序算法
冒泡排序
- 最低最稳定的排序算法
- 时间复杂度为: O(n^2)
- 实现思路为:
- 第一层循环决定比较次数
- 第二层循环进行排序规则的定义
- 实现思路为:
javascript
//外部自定义排序函数
function bubbleSort(arr, callback) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // 排序论数
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) { // 比较次数
let flag = false;
if (callback(arr[j], arr[j + 1])) {
[arr[j], arr[j + 1]] = [arr[j + 1], arr[j]];
flag = true;
}
}
if (!flag) {
break;
}
}
}
function descSort(a, b) {
return a > b;
}
function ascSort(a, b) {
return a < b;
}typescript
type CallbackType = <T>(arr: T[], a: T, b: T) => boolean;
function swap(arr: number[], i: number, j: number) {
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]];
}
function bubbleSort(arr: number[], callback: CallbackType<number>) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // 排序论数
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) { // 比较次数
let flag = false;
if (callback(arr, j, j + 1)) {
swap(arr, j, j + 1)
flag = true;
}
}
if (!flag) {
break;
}
}
}
function descSort(arr: number[], a: number, b: number): CallbackType<number> {
return arr[a] > arr[b];
}
function ascSort(arr: number[], a: number, b: number): CallbackType<number> {
return arr[a] < arr[b];
}选择排序
- 选择排序的效率是十分高的呐
- 时间复杂度为: O(n^2)
- 实现思路
- 选定一个索引位置,然后和后面的元素进行一次比较
- 如果后面的元素小于前面的元素,那么就将后面的元素和前面的元素进行交换
- 循环结束后,就找到了最小的元素,然后将最小的元素和第一个元素进行交换
- 循环结束后,就找到了最大的元素,然后将最大的元素和最后一个元素进行交换
typescript
function selectionSort(arr: number[]) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let index = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[index] > arr[j]) {
index = j
}
}
if (index !== i) {
[arr[i], arr[index]] = [arr[index], arr[i]]
}
}
}插入排序
- 插入排序的效率十分的高
- 时间复杂度为: O(n^2)
- 实现思路
- 局部有序性
- 对于插入排序而言的话,局部越有序,时间复杂度越低
- 从第一个元素开始,该元素已经被认为是局部有序的了
- 获取下一个元素,在已经排序了的元素后直接进行向前扫描
- 如果当前元素小于等于已经排序的元素,那么就将当前元素插入到已经排序的元素后面
- 局部有序性
typescript
function insertionSort(arr: number[]) {
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
let temp = arr[i];
//todo core code
let j = i
while (arr[j - 1] > temp && j > 0) {
arr[i] = arr[j - 1]
j--
}
arr[j] = temp
}
return arr
}希尔排序
- 希尔排序是插入排序的改进版
- 希尔排序的时间复杂度为: O(n^2)
- 实现思路
- 选择间隔序列
- 分组排序
- 缩小间隔
- 最终排序
typescript
function shellSort(arr: number[]): void {
let n = arr.length;
let gap = Math.floor(n / 2);
while (gap > 0) {
for (let i = gap; i < n; i++) {
let temp = arr[i];
let j = i;
while (j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp) {
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
j -= gap;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
// 缩小间隔
gap = Math.floor(gap / 2);
}
}归并排序
- 归并排序是分治算法的一种
- 时间复杂度为: O(nlogn)
- 实现思路
- 分解:递归地将数组分成两个子数组,直到每个子数组的长度为1
- 合并:将两个有序的子数组合并成一个有序的数组
typescript
function mergeSort(arr: number[]): number[] {
if (arr.length <= 1) {
return arr;
}
// 找到中间位置
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
// 递归地对左右子数组进行排序
const left = mergeSort(arr.slice(0, mid));
const right = mergeSort(arr.slice(mid));
// 合并两个有序的子数组
return merge(left, right);
}
function merge(left: number[], right: number[]): number[] {
let result: number[] = [];
let leftIndex = 0;
let rightIndex = 0;
// 比较两个子数组的元素,将较小的元素放入结果数组中
while (leftIndex < left.length && rightIndex < right.length) {
if (left[leftIndex] < right[rightIndex]) {
result.push(left[leftIndex]);
leftIndex++;
} else {
result.push(right[rightIndex]);
rightIndex++;
}
}
// 将剩余的元素放入结果数组中
return result.concat(left.slice(leftIndex)).concat(right.slice(rightIndex));
}快速排序
typescript
function quickSort(arr: number[], left: number = 0, right: number = arr.length - 1): void {
if (left < right) {
// 获取分区点
const pivotIndex = partition(arr, left, right);
// 对左子数组进行快速排序
quickSort(arr, left, pivotIndex - 1);
// 对右子数组进行快速排序
quickSort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, right);
}
}
function partition(arr: number[], left: number, right: number): number {
// 选择最右边的元素作为基准
const pivot = arr[right];
let i = left - 1;
for (let j = left; j < right; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]]; // 交换元素
}
}
// 将基准元素放到正确的位置
[arr[i + 1], arr[right]] = [arr[right], arr[i + 1]];
return i + 1;
}基数排序
typescript
function radixSort(arr: number[]): number[] {
if (arr.length === 0) return arr;
// 找到数组中的最大值,确定最大位数
const max = Math.max(...arr);
const maxDigits = max.toString().length;
// 从最低位到最高位进行排序
for (let digit = 0; digit < maxDigits; digit++) {
// 创建10个桶,用于存储每一位的数字
const buckets: number[][] = Array.from({ length: 10 }, () => []);
// 将数组中的每个数字放入对应的桶中
for (const num of arr) {
// 获取当前位的数字
const digitValue = Math.floor((num / Math.pow(10, digit)) % 10);
buckets[digitValue].push(num);
}
// 将桶中的数字按顺序放回数组
let index = 0;
for (const bucket of buckets) {
for (const num of bucket) {
arr[index++] = num;
}
}
}
return arr;
}